Ear Phone ODM
About Speaker
History of Speakers


Music, the art of sound that has been walked along with human history, has become an eternal companion to mankind since the invention of Graham Bell's telephone in the United States in 1876 and Edison's phonograph using the telephone principle.
The invention of the phonograph after recording the first human voice on Earth was a great step in the creation of today's 'audio engineering'.
At that time, people doubted their ears and even thought that there was a devil in them.It was a phonograph with a simple structure that was not interesting, but it was shocking enough to go beyond human imagination.
As the phonograph released by Edison received favorable reviews from many people, the "Ediso phonograph company" was established.However, the sound played was so primitive that Edison was immersed in the study of incandescent bulbs that the phonograph did not develop any further.
The phonograph began to change by some people who were interested in it.Among them, Emile Berlina is a person who made cylinder records that were made of bells in the same form as they are today.
Chichester Bell (Graham Bell's nephew) and Sennodont, a Volta lab run by Graham Bell (1847-1922), became interested in Edison's phonograph made of cherry powder.
Instead of bells, they began carving sound into a round barrel made of wax.At this time, Emil Berlina intervened in this, and the history of phonograph began to enter a new phase.
On May 4, 1886, the Volta Institute received an improved Phonograph patent and proposed Edison to work with more advanced devices.However, Edison, angry at stealing his own and even patenting it, refused, and he finally completed the improved phonograph in five days, as if he were madly immersed in improved phonograph research, which was "M(E) type."
The following year, young scientist Emile Berlina did not like the cylindrical phonograph, so she wanted to record it because it could reduce sonic vibration. That's why a "grammophon" was developed using a method in which a glass disk rotates under a fixed needle and the oil film applied to the surface is peeled off by the vibration of the needle.
As a result, the phonograph industry gradually began to show its true value as it became possible to reproduce records that were impossible.In the United States, Edison's phonograph and Berlina's Gramophone began a fierce battle over the same market from the beginning.
Lippincourt, who started the phonograph industry with Edison, eventually established the North American phonograph company on July 14, 1888, creating the first company.The Jukebox, a modified version of Edison's Class M, revitalized the fairly demanding phonograph by inserting a five-cent coin and then changing the handle lightly.
Berlina and Eldridge Johnson founded Victor Talking Co. and developed a convenient and highly innovative spring motor type that uses only the advantages of Edison and Berlina Ta.
Meanwhile, the sensational popularity of records, or Red Label, made by a record store owner in St. Petersburg was great.Edison changed the needle into a diamond and created a diamond disc phonograph to make the sound played on the phonograph prettier.
The Diamond Disk Chipendale, released in 1912, has a lever attached to the rotating plate at a high speed of 80 degrees of rotation using grouting, allowing the volume to be adjusted.
In 1900, the recorder was made by Dr. Waldmarforzen.The Glee recording method was inspired by the way it was recorded on steel wires when sending signals directly through electromagnets with the phone microphone.
How does the Speaker work?
Hearing, one of the five basic senses that humans have since birth, is a structure in which the source of sound vibrates the medium of air in the form of sound waves and is transmitted to the brain through the auditory organs inside the human ear.
Speakers convert electrical signals, which are media that generate sound, into kinetic energy by the principle of induction electrons, and vibrate a diaphragm made of various materials, creating sound waves in the air and reaching the human ear.
Since Edison invented the phonograph, the science of sound has developed rapidly, and speakers have become popular.
Electricity flows around the wire, creating a magnetic field. You can see that the magnetic field creates a force, as you can see from the movement of the needle in the compass. In addition, as the direction of flow through the coil-wound wire changes, the N pole and the S pole intersect each other, and the direction changes, and the force to push and pull is applied, causing the electromagnet to move.
There is something called a diaphragm on the speaker. If you attach a coil (voice coil) to this diaphragm, attach a permanent magnet, and send a current, the coil is forced to move back and forth, and the movement is transmitted to the diaphragm to vibrate the air. This is the principle of speakers.
Speakers are classified in various ways depending on how the diaphragm is raised. Among them, the most classic and first invented one is the dynamic speaker. Dynamic speakers are made up of permanent magnets, plates, call-piece dampers, and the voice you hear moves in different patterns and shapes depending on the strength of the electrical flow and the direction of the periodically changing magnetic field.
If you can make a high note when the frequency increases, you can make a low note if you write it down. And the larger the vibrating width of the diaphragm, the stronger the sound can be made.Applying Fleming's left hand law makes it easier to understand the direction of the finger if you can tell the direction of the force depending on the direction of the current.
Although there are many different shapes of the diaphragm, it usually takes a conical (con) shape. Depending on how electrical signals are transformed into sound waves, they can be classified into electrostatic, electromagnetic, dynamic, magnetic distortion, etc. Among these type dynamic one that has been most commonly used for music and voice playback that humans can hear is the most commonly used.
All sound-producing speaker devices such as earphones, headphones, and industrial speakers play a role in creating sound waves that can be heard by humans by converting electrical signals into kinetic energy with the same structure and principle.
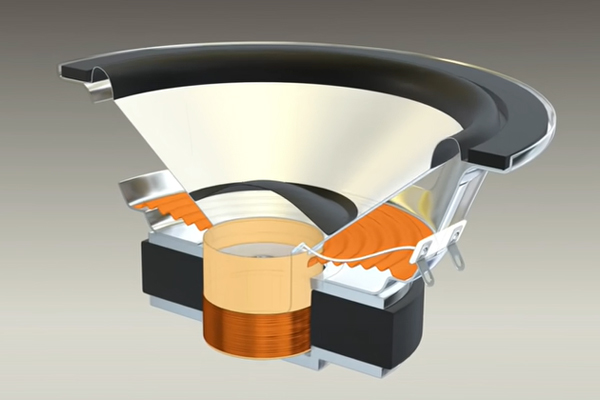
Main parts of speaker
The diaphragm (con) is - a key element in generating sound. When the voice coil attached to the diaphragm vibrates, the diaphragm vibrates and vibrates the air so that people can hear it. The main materials include paper, synthetic resin, rubber, pulp, talc, mica, graphite, glass fiber, and aluminum. Corn paper is used the most, but it has a weakness that is vulnerable to moisture.
- Voice coil A copper wire wound around a bobbin. Voice signals are received and transmitted to the diaphragm, and the higher the density of winding, the better the quality of sound. When a current flows through the voice coil, a magnet property is created, and a force is generated by the intersection of the N pole and the S pole with the permanent magnet, thereby transmitting a force pushing and pulling the diaphragm.
- Edge A device that supports a diaphragm and is a part that makes the voice coil and the diaphragm move left and right. Nowadays, rubber or synthetic resin is used rather than paper.
- Permanent magnet When a current flows in the voice coil, a magnetic field is created, and the permanent magnet and the N and S poles are reversed depending on the direction of the current to help move up and down. Magnets affect negative pressure and vibration depending on the type.
- Gasket It is between the edge and the frame, and serves to fix the edge so that it does not deviate from the unit.
- Damper It is located between the diaphragm and the voice coil and secures the diaphragm in a stable manner, and adjusts the vibration well without detaching the diaphragm.
- Frame It maintains the framework of the speaker unit and serves to fix the unit. It is mainly made using metal or synthetic resin.
- Dust Cap Prevent foreign substances from entering the speaker inside.
- Plate It blooms inside the voice coil and is made of a material that keeps the voice coil stable and allows magnetic force.
- Pole piece it Collects magnetic fields generated by voice coils.
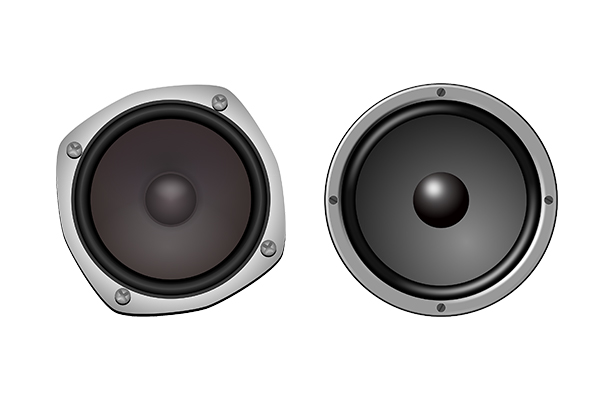


Various Classification of speakers
A speaker is a sound device that converts electrical energy into kinetic energy and vibrates air in the form of sound waves through a diaphragm to transmit voice, music, and other effective signals to people. Speakers are used for various purposes and purposes in various places. Speakers can be divided into different categories according to different classification criteria. Personal earphones, headphones, and smartphones also use speakers, and they can be used for a variety of purposes, including computers, audio equipment, medical devices, military and industrial purposes. Speakers can be classified in various ways depending on the placement of speakers, speaker size, unit shape, sound playback band and enclosure shape. Depending on the material and components of the speaker, the speaker can be used for different purposes, and the structure, durability, and output of the drive vary greatly.


Speaker Size Classification
Although there is no exact standard for classification by speaker size, it is a classification used because the number of units mounted is usually determined by the speakers.
- Satellite speakers Relatively recent English. It is a speaker smaller than a book self speaker and is very small in size, making it difficult to play. Since there is no woofer for low-pitched playback, it is small in size, easy to store, and has the advantage of being free to store and move.
- Book Self Speaker Literally means a bookshelf. It refers to a size that can be put on a shelf, and is mainly a speaker with a height of less than 50cm and a woofer unit of less than 8 inches.
- Tall Boy Speaker Means a speaker the size of a child's height. Usually, the size is less than 1.5 meters, and if the book self speaker is a two-way method, the tall boy speaker can be 3 wedges long and you can hear rich sounds until the ultra-low sound area.
- Floor standing speakers The most expensive speakers in size because they are large and tall, and the enclosure is very large. The composition and material of the enclosure are very complex and classified as professional speakers.
Classification by sound range
- Twitter High-pitched speaker. A small bird chirps, using a lightweight diaphragm to produce a high-pitched sound over 3Khz. It's usually a small size, 1 to 2 inches.
- Super-weeter Play instruments up to 50 Khz to compensate for the lack of high-pitched playback of Twitter speakers.
- Mid-Range A medium-range speaker, usually about 4 inches in size. It's an important element in musical performance.
- Mid-Woofer The diaphragm is a cone-shaped speaker that produces sound in the mid-to-low range, also known as the mid-base.
- Sub-Woofer A speaker with the lowest low-pitched sound, measuring about 15 inches in size and producing a low-pitched sound of less than 100 Hz.
- Full-Range The speaker is literally a speaker that produces a full range of sound from low to high range.
Multi-way speakers are divided into different frequency bands of different sizes and played back by different drivers. Increases sound clarity over full-range speakers.
Classification by the shape of the diaphragm
- Cone-type speakers As speakers became common, they were the first to be developed, and speakers in the belly, such as low-end, high-end, high-pitched, and low-pitched, are in this form.
- Dome type speaker The shape of the speaker is called a dome type speaker because it has a round roof. The diaphragm has a small structure and is mainly used for high-pitched sounds.
- Horn type speaker The name is given because the diaphragm has a horn shaped like a trumpet. The second-hand station makes a sound. It is a speaker designed to convey sound to people far away.
Classification by the back space of the diaphragm
- Open speaker The back of the diaphragm of the speaker is an open space, so there is no echo at all. Therefore, there is no diffraction of sound waves due to sound reflection, so the purest sound can be made.
- Closed speaker The vibrator of the speaker is trapped in the enclosure (sound canister), so the vibrator's vibration has little effect on the outside.Sound absorption material is usually placed inside the enclosure because the echo inside the speaker may be restricted.
- Bass-reflex Speakers A method for using only low-pitched sounds and eliminating high-pitched sounds in the form of holes drilled to reuse low-pitched sounds resonated inside the enclosure.
Classification by Amplification Method
- Passive Speakers Most speaker formats we encounter. Power is supplied by an external amplifier. Therefore, it is connected to a speaker wire running on the amplifier to receive power without requiring power.You can place your speakers relatively freely.If you want to select the preamplifier, power amplifier, and equalizer, you can also select a more modular setting.
- Active Speaker A separate power supply must be entered into the speaker to activate the amplifier. It's definitely easier to use than passive speakers and there's no need to match the internal amplifier with the speaker. The biggest advantage of active speakers is that they don't need amplifiers or Bluetooth receivers with built-in wireless connections, and they can accept wireless signals. No amplifiers or receivers are required, saving money over passive speakers.